Title: Micro-Unit Living: The Future of Urban Real Estate
Introduction: In today's rapidly evolving urban landscape, a new trend is reshaping the way city dwellers think about home. Micro-unit living, once considered a niche market, is now at the forefront of urban real estate innovation. These compact living spaces, typically ranging from 200 to 400 square feet, are revolutionizing city housing and challenging traditional notions of what constitutes a comfortable home. As urban populations grow and housing affordability becomes increasingly strained, micro-units offer a creative solution that's catching the attention of developers, investors, and residents alike.
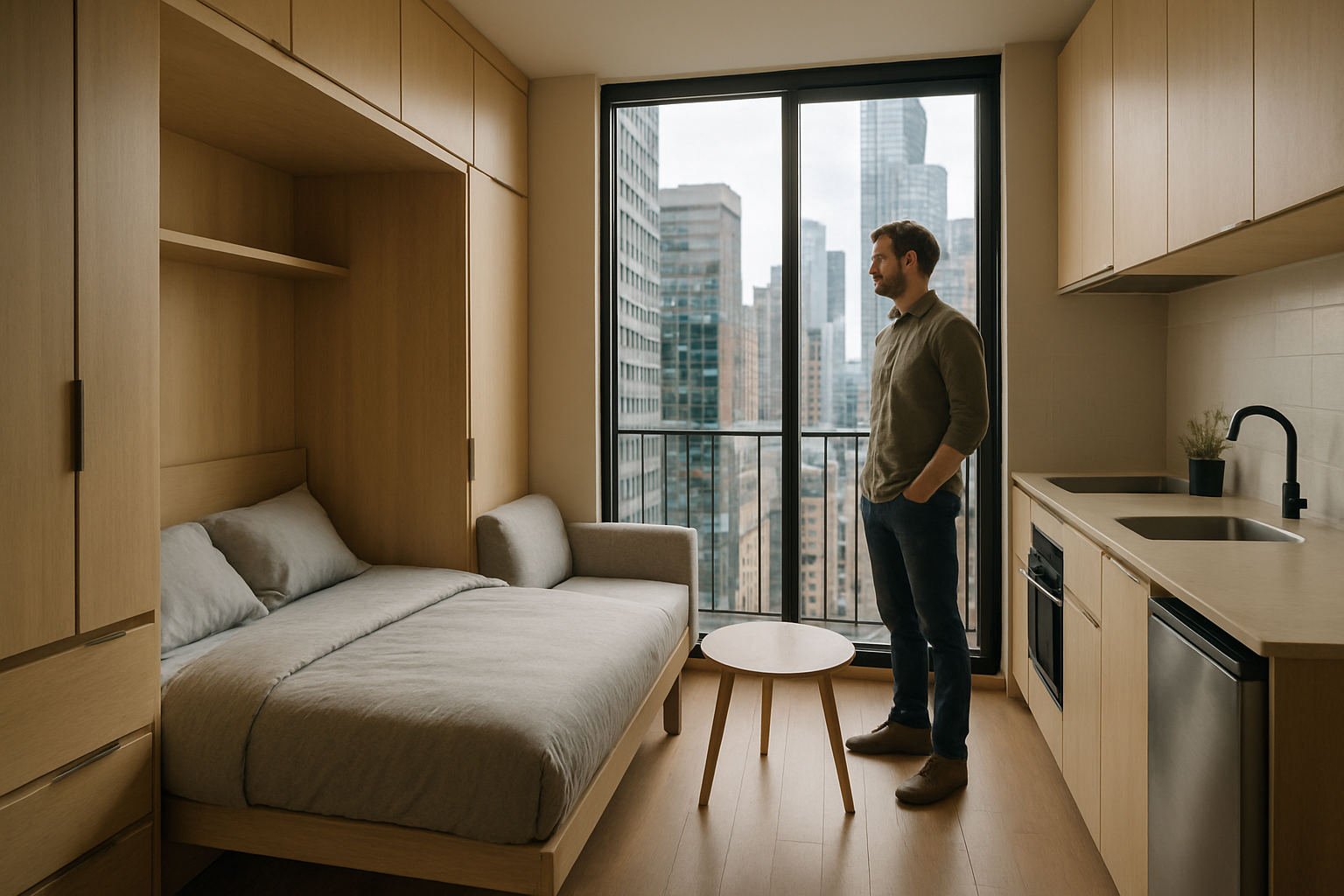

Young professionals, in particular, are drawn to micro-units for their affordability and prime locations. These compact spaces often come with lower rent prices compared to traditional apartments, allowing residents to live in desirable neighborhoods that might otherwise be out of reach. Moreover, the minimalist lifestyle associated with micro-living aligns well with the values of many millennials and Gen Z individuals who prioritize experiences over possessions.
Design Innovations in Micro-Units
The success of micro-unit living hinges on intelligent design. Architects and interior designers are pushing the boundaries of spatial efficiency, creating living spaces that feel much larger than their square footage suggests. Multi-functional furniture, such as murphy beds that transform into desks or dining tables, maximizes the utility of every inch.
High ceilings and large windows are common features in well-designed micro-units, creating a sense of openness and bringing in natural light. Some developments incorporate shared amenities like rooftop gardens, co-working spaces, and communal kitchens, extending the living space beyond the unit itself. These common areas not only provide additional functional space but also foster a sense of community among residents.
Financial Implications for Investors and Developers
From an investment perspective, micro-units present an intriguing opportunity. While the cost per square foot to develop these units is typically higher than traditional apartments, the potential returns can be substantial. In many markets, micro-units command higher rents per square foot than their larger counterparts, translating to better yields for investors.
Developers are finding that micro-unit projects can be particularly profitable in urban areas with high land costs. By increasing the number of units in a given footprint, they can maximize the return on their investment. However, it’s crucial for investors to carefully consider local zoning laws and building codes, as some municipalities have restrictions on minimum unit sizes or maximum occupancy rates.
Impact on Urban Planning and Development
The proliferation of micro-units is reshaping urban development strategies. City planners are reassessing zoning laws and building codes to accommodate this new housing typology. Some cities, recognizing the potential of micro-units to address housing shortages, have adjusted minimum unit size requirements or created special zoning districts to encourage their development.
Micro-unit developments can contribute to urban density without drastically altering neighborhood character, as they often involve the adaptive reuse of existing buildings or infill development on small lots. This approach aligns well with smart growth principles and can help cities accommodate population growth without extensive outward expansion.
Challenges and Considerations
While micro-unit living offers numerous benefits, it’s not without challenges. Critics argue that these small living spaces may negatively impact residents’ quality of life, potentially leading to feelings of claustrophobia or social isolation. There are also concerns about the long-term sustainability of micro-units, questioning whether they can adapt to changing life stages and family structures.
From a regulatory standpoint, some cities have encountered pushback from community groups worried about overcrowding and strain on local infrastructure. Balancing the need for affordable housing options with community concerns remains an ongoing challenge for policymakers and developers alike.
The Future Outlook for Micro-Unit Living
As urban populations continue to grow and housing affordability remains a pressing issue, micro-unit living is likely to play an increasingly significant role in the real estate landscape. Advancements in modular construction techniques may further streamline the development process, potentially reducing costs and expanding the market for these compact homes.
The COVID-19 pandemic has raised questions about the viability of dense urban living, but early indications suggest that the demand for micro-units remains strong. The flexibility and affordability they offer may become even more attractive in a post-pandemic economy where remote work is more prevalent, allowing residents to prioritize location over space.
In conclusion, micro-unit living represents a dynamic and innovative approach to urban housing challenges. As this trend continues to evolve, it will likely reshape not only how we think about personal living spaces but also the broader dynamics of urban development and community planning. For investors, developers, and city dwellers alike, micro-units offer a compelling vision of the future of urban real estate.